AR.js - Augmented Reality on the Web

AR.js is a lightweight library for Augmented Reality on the Web, which includes features like Image Tracking, Location based AR and Marker tracking.
Location Based documentation updated and enhanced for AR.js 3.4
What Web AR means (Augmented Reality on the Web)
Augmented Reality is the technology that makes possible to overlay content on the real world. It can be provided for several type of devices: handheld (like mobile phones), headsets, desktop displays, and so on.
For handheld devices (more generally, for video-see-through devices) the 'reality' is captured from one or more cameras and then shown on the device display, adding some kind of content on top of it.
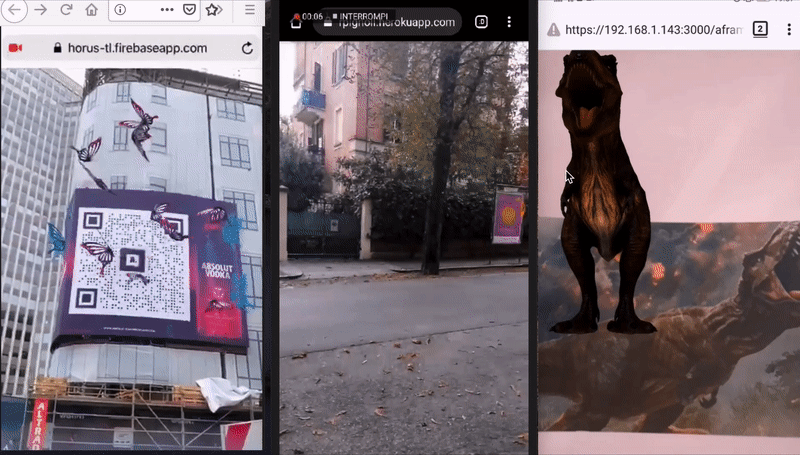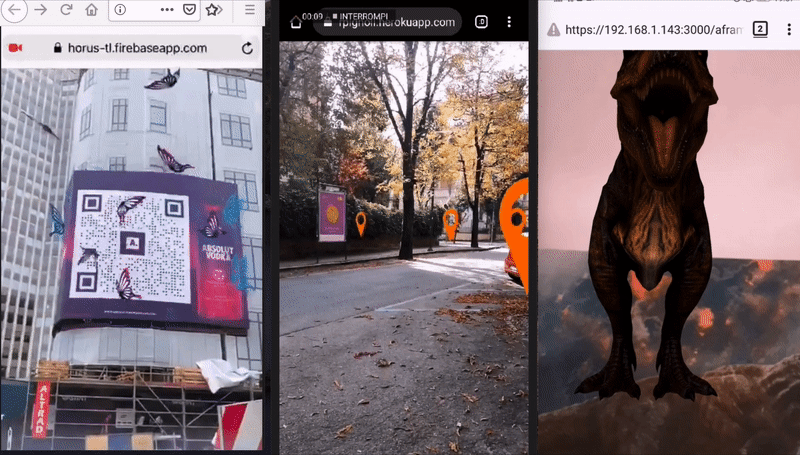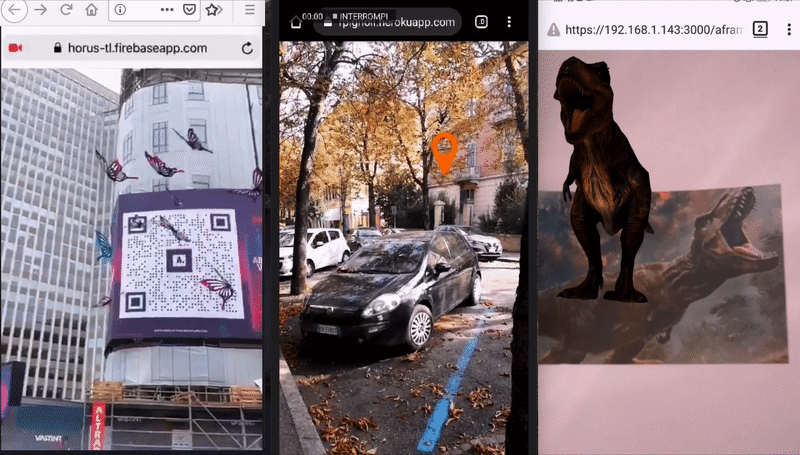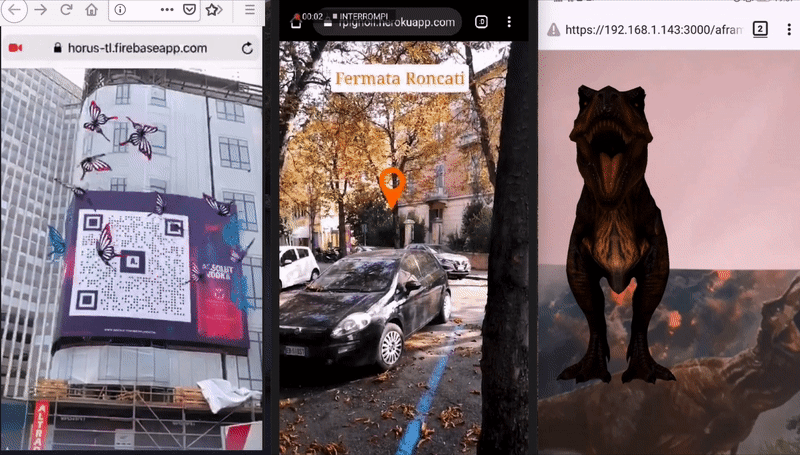
For developers, to develop Augmented Reality ('AR' from now on) on the Web, means to avoid all the Mobile app development efforts and costs related to App stores (validation, time to publish). It also means to re-use well known technologies like Javascript, HTML and CSS, familiar to a lot of developers and possibly designers.
It basically means that it is possible to release every new version instantly, fix bugs or release new features in near real-time, opening a lot of practical possibilities.
For users, it means to reach an AR experience just visiting a website. As QR Codes are now widespread, it's also possible to scan a QR Code and reach the URL without typing. Additionally, users do not have to reserve storage space on their download the AR app, and do not have to keep it updated.
Why AR.js
We believe in the Web, as a collaborative and accessible environment. We also believe in Augmented Reality technology, as a new communication medium, that can help people see reality in new, exciting ways. We see Augmented Reality (AR) used everyday for a lot of useful applications, from art, to education, also for fun.
We strongly believe that such a powerful technology, that can help people and leverage their creativity, should be free in some way. Also collaborative, if possible. And so, we continue the work started by Jerome Etienne, in bringing AR on the Web, as a free and Open Source technology.
Thank you for being interested in this, if you'd like to collaborate in any way, contact us (https://twitter.com/nicolocarp).
The project is now under a Github organization, that you can find at https://github.com/ar-js-org and you can ask to be part of it, for free.
AR types
AR.js features the following types of Augmented Reality, on the Web:
-
Image Tracking, when a 2D images is found by the camera, it's possible to show some kind of content on top of it, or near it. The content can be a 2D image, a GIF, a 3D model (also animated) and a 2D video too. Cases of use: Augmented Art, learning (Augmented books), Augmented flyers, advertising, etc.
-
Location Based AR, this kind of AR uses real-world places in order to show Augmented Reality content, on the user device. The experiences that can be built with this library are those that use a user's position in the real world. The user can move (ideally outdoor) and through their smartphones they can see AR content where places are in the real world. Moving around and rotating the phone will make the AR content change according to users position and rotation (so places are 'anchored' in their real position, and appear bigger/smaller according to their distance from the user). With this solution it’s possible to build experiences like interactive support for tourist guides, assistance when exploring a new city, find places of interest like buildings, museums, restaurants, hotels and so on. It’s also possible to build learning experiences like treasure hunts, and biology or history learning games, or use this technology for situated art (visual art experiences bound to specific real world coordinates).
-
Marker Tracking, When a marker is found by the camera, it's possible to show some content (same as Image Tracking). Markers are very stable but limited in shape, color and size. It is suggested for those experiences where are required a lot of different markers with different content. Examples of use: (Augmented books), Augmented flyers, advertising.
Key points
- Very Fast : It runs efficiently even on phones
- Web-based : It is a pure web solution, so no installation required. Fully javascript based, using three.js + A-Frame + jsartoolkit5
- Open Source : It is completely open source and free of charge!
- Standards : It works on any phone with webgl and webrtc
AR.js has reached version 3. This is the official repository: https://github.com/AR-js-org/AR.js. If you want to visit the old AR.js repository, here it is: https://github.com/jeromeetienne/AR.js.
Import the library
AR.js from version 3 has a new structure.
AR.js comes in two, different builds. They are both maintained. They are exclusive.
The file you want to import depends on what features you want, and also which render library you want to use (A-Frame or three.js).
AR.js uses jsartoolkit5 for tracking, but can display augmented content with either three.js or A-Frame.
You can import AR.js in one version of your choice, using the <script> tag on your HTML.
The examples below assume the latest version of AR.js from the master branch, but you can replace master with a specific version, e.g. 3.4.5 for the latest version.
AR.js with Image Tracking
Import AFRAME version:
<script src="https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/master/aframe/build/aframe-ar-nft.js">
Import three.js version:
<script src="https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/master/three.js/build/ar-nft.js">
AR.js with Marker Tracking
Import AFRAME version:
<script src="https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/master/aframe/build/aframe-ar.js">
Import three.js version:
<script src="https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/master/three.js/build/ar.js">
If you want to import a specific version, you can do that easily replacing master with the version tag, e.g.:
<script src="https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/3.0.0/aframe/build/aframe-ar-nft.js">
Location-based AR.js
For the A-Frame version, it's recommended to use version 3.4.5, rather than master:
<!-- A-Frame itself -->
<script src="https://aframe.io/releases/1.3.0/aframe.min.js"></script>
<!-- Pure three.js code that the A-Frame components use for location-based AR -->
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/3.4.5/three.js/build/ar-threex-location-only.js'></script>
<!-- AR.js A-Frame components -->
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/3.4.5/aframe/build/aframe-ar.js'></script>
For the three.js version, it's recommended to use the new AR.js project LocAR instead of the main repository.
Requirements and Known Issues
Some requirements and known issues are listed below:
- It works on every phone with webgl and webrtc.
- Marker based tracking is very lightweight, while Image Tracking is more CPU consuming
- You must ensure that you have matching versions of AR.js and A-Frame. AR.js 3.4.5 (the latest version) requires A-Frame 1.3.0 while AR.js 3.4.4 and below requires 1.0.4.
- Location-based AR will not work correctly on Firefox, due to the inability to obtain absolute device orientation (compass bearing)
- On Android/Chrome, you may encounter issues with location-based AR due to inaccuracies in compass calibration (incorrect north). This is likely to be a hardware limitation of the device.
- On some phones you may encounter problems with locating North due to inherent miscalibrations of the device sensors. This is a known problem recognised by the three.js developers: see here
- Please ensure you enable high accuracy location for your selected browser on Android. Sometimes high accuracy location is turned off by default, and this will lead to an inaccurate GPS location.
- There is currently a bug in location-based AR where the camera feed is stretched away from the centre of the screen, meaning that there is reduced accuracy in placement of objects further away from the centre. Work is ongoing to investigate this.
- On device with multi-cameras, Chrome may have problems on detecting the right one. Please use Firefox if you find that AR.js opens on the wrong camera. There is an open issue for this.
- To work with Location Based feature, your device needs to have GPS, accelerometer and magnetometer sensors. It will not work if any of these sensors are absent.
- Please, read carefully any suggestions that AR.js pops-up -as alerts- for Location Based on iOS, as iOS requires user actions to activate geoposition Access to the phone camera or to camera GPS sensors, due to major browsers restrictions, can be done only under https websites.
All the examples you will see, and all AR.js web apps in general, have to be run on a server. You can use local server or deploy the static web app on the web.
Always deploy under https
So don't forget to always run your examples on secure connections servers or localhost. Github Pages is a great way to have free and live websites under https.
Getting started
Here we present three, basic examples, one for each AR feature. For specific documentation, on the top menu you can find every section, or you can click on the following links:
Image Tracking Example
There is a Codepen for you to try. Below you can find also a live example.
Please follow these simple steps:
- Create a new project with the code below (or open this live example and go directly to the last step)
- Run it on a server
- Open the website on your phone
- Scan this picture to see content through the camera.
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/aframevr/aframe@1c2407b26c61958baa93967b5412487cd94b290b/dist/aframe-master.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/master/aframe/build/aframe-ar-nft.js"></script>
<style>
.arjs-loader {
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.8);
z-index: 9999;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.arjs-loader div {
text-align: center;
font-size: 1.25em;
color: white;
}
</style>
<body style="margin : 0px; overflow: hidden;">
<!-- minimal loader shown until image descriptors are loaded -->
<div class="arjs-loader">
<div>Loading, please wait...</div>
</div>
<a-scene
vr-mode-ui="enabled: false;"
renderer="logarithmicDepthBuffer: true;"
embedded
arjs="trackingMethod: best; sourceType: webcam;debugUIEnabled: false;"
>
<!-- we use cors proxy to avoid cross-origin problems -->
<!--
⚠️⚠️⚠️
https://arjs-cors-proxy.herokuapp.com/ is now offline, Heroku has dismissed all his free plans from November 2022.
You need to host your own proxy and use it instead. The proxy is based on CORS Anywhere (see https://github.com/Rob--W/cors-anywhere).
⚠️⚠️⚠️
-->
<a-nft
type="nft"
url="https://arjs-cors-proxy.herokuapp.com/https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/master/aframe/examples/image-tracking/nft/trex/trex-image/trex"
smooth="true"
smoothCount="10"
smoothTolerance=".01"
smoothThreshold="5"
>
<a-entity
gltf-model="https://arjs-cors-proxy.herokuapp.com/https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/master/aframe/examples/image-tracking/nft/trex/scene.gltf"
scale="5 5 5"
position="50 150 0"
>
</a-entity>
</a-nft>
<a-entity camera></a-entity>
</a-scene>
</body>
Location Based Example
This example retrieves your position and places a red box near you.
Please follow these simple steps:
- Create a new project with the following snippet, and change
add-your-latitudeandadd-your-longitudewith a point very close to your latitude and longitude (about 0.001 degrees distant for both latitude and longitude), without the<>. - Run it on a server
- Activate GPS on your phone and navigate to the example URL
- Look around. You should see the box close to you, appearing in the requested position, even if you look around and move the phone.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>AR.js A-Frame Location-based</title>
<script src="https://aframe.io/releases/1.3.0/aframe.min.js"></script>
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/3.4.5/three.js/build/ar-threex-location-only.js'></script>
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/3.4.5/aframe/build/aframe-ar.js'></script>
</head>
<body>
<a-scene vr-mode-ui='enabled: false' arjs='sourceType: webcam; videoTexture: true; debugUIEnabled: false' renderer='antialias: true; alpha: true'>
<a-camera gps-new-camera='gpsMinDistance: 5'></a-camera>
<a-entity material='color: red' geometry='primitive: box' gps-new-entity-place="latitude: <add-your-latitude>; longitude: <add-your-longitude>" scale="10 10 10"></a-entity>
</a-scene>
</body>
</html>
This is just a basic example and most location-based applications will involve JavaScript coding. So, if you want to enhance and customize your Location Based experience, take a look at the Location Based docs.
Marker Based Example
Please follow these simple steps:
- Create a new project with the code below (or open this live example and go directly to the last step)
- Run it on a server
- Open the website on your phone
- Scan this picture to see content through the camera.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<script src="https://aframe.io/releases/1.3.0/aframe.min.js"></script>
<!-- we import arjs version without NFT but with marker + location based support -->
<script src="https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/master/aframe/build/aframe-ar.js"></script>
<body style="margin : 0px; overflow: hidden;">
<a-scene embedded arjs>
<a-marker preset="hiro">
<!-- we use cors proxy to avoid cross-origin problems -->
<!--
⚠️⚠️⚠️
https://arjs-cors-proxy.herokuapp.com/ is now offline, Heroku has dismissed all his free plans from November 2022.
You need to host your own proxy and use it instead. The proxy is based on CORS Anywhere (see https://github.com/Rob--W/cors-anywhere).
⚠️⚠️⚠️
-->
<a-entity
position="0 0 0"
scale="0.05 0.05 0.05"
gltf-model="https://arjs-cors-proxy.herokuapp.com/https://raw.githack.com/AR-js-org/AR.js/master/aframe/examples/image-tracking/nft/trex/scene.gltf"
></a-entity>
</a-marker>
<a-entity camera></a-entity>
</a-scene>
</body>
</html>
Advanced stuff
AR.js offers two ways, with A-Frame, to interact with the web page: to interact directly with AR content and Overlayed DOM interaction.
Also, there are several Custom Events triggered during the life cycle of every AR.js web app.
You can learn more about these aspects on the UI and Events section.
AR.js architecture
AR.js uses jsartoolkit5 for tracking, but can display augmented content with either three.js or A-Frame.
three.js folder contains
- source code for AR.js core, Marker based and Image Tracking
- examples for AR.js three.js based
- build for three.js AR.js based
- vendor stuff (jsartoolkit5)
- workers (used for Image Tracking).
When you find files that ends with -nft suffix, they're bundled only with the Image Tracking version.
A-Frame version of AR.js uses three.js parts as its core. A-Frame code, on AR.js, is simply a wrapper to write AR with Custom Components in HTML.
aframe folder contains
- source code for AR.js A-Frame (aka wrappers for Marker Based, Image Tracking components)
- source code for Location Based
- build for A-Frame AR.js based
- examples for A-Frame AR.js.
Tutorials
There are various tutorials available for developing with AR.js. These include:
Location Based
- Build your Location-Based Augmented Reality Web App: covers location-based AR.js with A-Frame.
- Develop a Simple Points Of Interest App (A-Frame version) (Provided with these docs): a further location-based A-Frame tutorial, written with AR.js 3.4 in mind.
- Develop a Simple Points of Interest App (LocAR.js version) (Provided with these docs): develop a points of interest app with the new LocAR.js API.
Troubleshooting, feature requests, community
You can find a lot of help on the old AR.js repositories issues. Please search on open/closed issues, you may find useful information.
Contributing
From opening a bug report to creating a pull request: every contribution is appreciated and welcome. If you're planning to implement a new feature or change the API please create an issue first. This way we can ensure that your precious work is not in vain.
Issues
If you are having configuration or setup problems, please post a question to StackOverflow. You can also address question to us in our Gitter chatroom
If you have discovered a bug or have a feature suggestion, feel free to create an issue on Github.
Submitting Changes
After getting some feedback, push to your fork and submit a pull request. We may suggest some changes or improvements or alternatives, but for small changes your pull request should be accepted quickly.
Some things that will increase the chance that your pull request is accepted:
- Follow the existing coding style
- Write a good commit message